Wake on LAN setup guide
WOL requires some setup, depending on the OS, and it has certain caveats that we explore in this guide.
We are going to review the following settings:
- Checking if WOL is supported;
- BIOS/UEFI setup;
- enabling network adapter options, depending on the OS;
- optional router setup for making a WOL call over the Internet;
- miscellaneous tweaks.
This guide is mostly about using this feature on a wired network. However, some wireless network adapters also support Wake on wireless LAN. It won't require any specific setup, and the procedure is often the same.
WARNING: using Wake On LAN will increase power usage when the device is off. This is important in case of mobile devices as it may cause battery drain.
Pre-check for WOL support
It is important to check that your hardware supports the necessary features. Most modern devices do. We’ll check the following options:
- BIOS/UEFI settings;
- network adapter driver options.
BIOS/UEFI setup
Open BIOS or UEFI settings. Find Wake on LAN and enable it. If you can’t find it, refer to the motherboard/laptop manual to find out if it’s supported.
Enable WOL in the operating system
When the OS shuts down, it sends signals that turn off all the hardware. The operating system is responsible for keeping network adapter powered on, so it may receive Magic Packet and power the system up. This section will describe how to enable this in Windows, Mac OS X and Linux.
Windows setup
1.Open Device Manager;
2.Find your network adapter and open Properties;
3.Open Advanced tab;
4.In the list, find Wake on Magic Packet and set Enabled (name of option may be different);
5.Next, open Power Management tab and enable the following options (if available):
- Allow this device to wake up the computer;
- Only allow a magic packet to wake the computer.
Find out the MAC address (a hint in case you rarely use Windows: run ipconfig /all then look for the Mac after Physical Address). Make sure you’re looking in the settings of the correct physical network adapter.
Settings in Windows 8, 8.1 and 10
The recent versions of Windows offer the Fast Startup feature to the users. This feature is NOT compatible with WOL, so it should be disabled.
Open Control Panel -> Power Options -> Choose what the power buttons do -> Change settings that are currently unavailable and disable Turn on fast startup, then click Save changes.
Mac OS X setup
To enable WOL on a Mac:
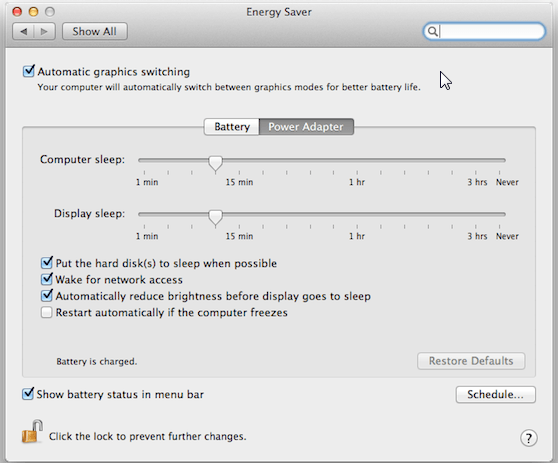
1.Open System Preferences;
2.Go to Energy Saver;
3.Enable Wake for network access. Depends on the specific system because it can have more than one network adapter.
To find the MAC address:
1.Open System Preferences;
2.Find and open Network;
3.Select Wi-Fi or Ethernet adapter and click on Hardware button;
4.Open Hardware tab and copy the MAC address.
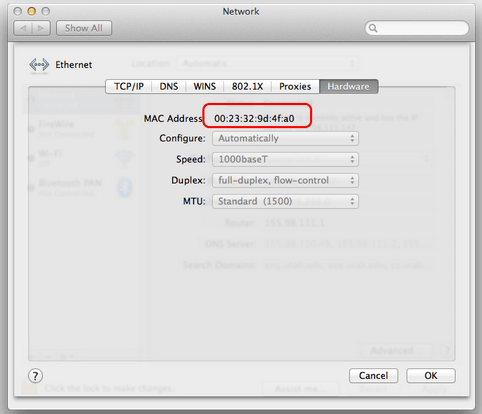
You will need the MAC address to wake the device.
GNU/Linux setup
In general, Linux setup may vary on different distributions. Our recommendations will mostly work until the first reboot only. They will help you make sure if your network adapter supports WOL and also test this feature. The best option to make it permanent is to follow the official or community documentation for a specific Linux flavor and the environment.
Requirements:
- root access;
- ethtool installed (often installed by default);
- Ethernet identifier such as eth0 or enp3s0.
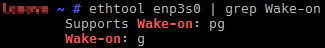
To check support for your card, open terminal emulator and type:
# ethtool eth0 | grep Wake-on
Supports Wake-on: pg
Wake-on: d
Supports Wake-on will list the supported modes. g is a required option. Wake-on shows the current status of the network adapter. To enable WOL, type the following command:
# ethtool -s eth0 wol g
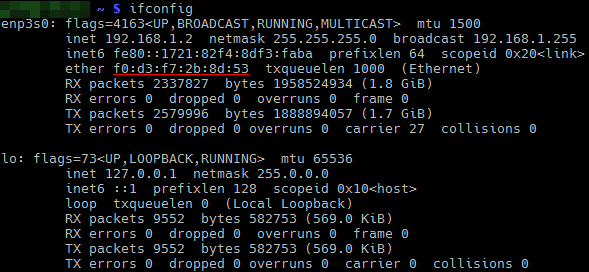
To find out the MAC address, type ifconfig and find it:
Wake on wireless LAN
Intel Centrino-compliant network adapters support Wake on wireless LAN except that this feature is unavailable in Windows XP (as explained in the drivers area on the official Intel website).
Windows 7, Linux and Mac OS X support this feature and the installation procedure is the same as above. Just be sure that you enabled Magic Packet on a proper device.
WOL over the Internet
In general, WOL is working over the Internet. In many cases it all depends on a specific network setup, and that of course involves router settings.
In many cases stock firmwares are primitive and offer only a limited feature set. Advanced and customized firmwares provide more settings.
We recommend following official or community guidelines for firmwares such as DD-WRT or OpenWRT.
In general, WOL over the Internet will require:
- setting a static IP address for your device;
- setting port forwarding to access the device behind NAT;
- router's public IP address or dynamic DNS setup to access the router from the Internet.
As an alternative, it is possible to connect to the router over SSH and then wake up the device using a wol utility on the router;
Sending the Magic Packet
To send a Magic Packet, you can use a software utility. Linux users may use wol (also possible to run on a router, but through an SSH channel).
Windows users may want to try WakeMeOnLan.
After all setup is completed, it's time to test wake on LAN by sending the Magic Packet. Be sure to specify the following information:
- MAC address;
- IP or domain address;
- subnet mask;
- port number if necessary.
Final Words
As of March 2018, DeskRoll does not implement Wake On LAN. On the other hand, Magic Packet sending utilities have been around for quite some time. Another consideration is that currently DeskRoll doesn’t require port configuration, as it works over the same ports as your browser. Wake On LAN would require additional ports which would cause unnecessary headache when using DeskRoll.
Also, waking your box from a device that’s on the same LAN is perfectly safe. You can do it over secure SSH or using DeskRoll (if you are waking your device from a PC).